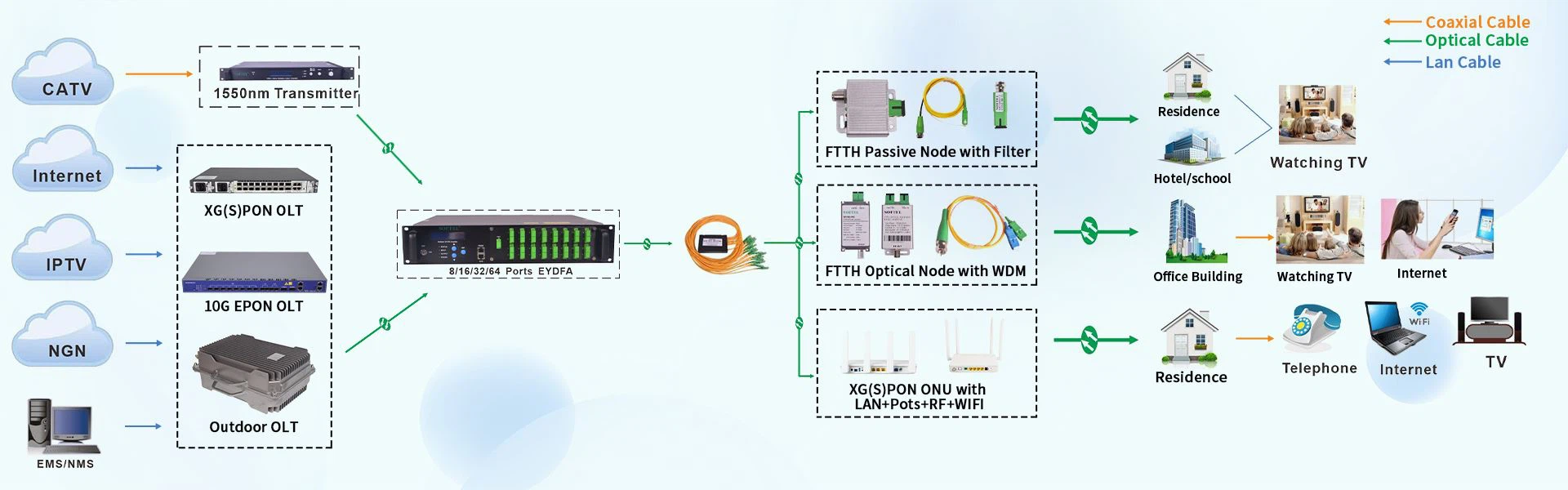
What is the difference between switched Ethernet networking and PON networking With more and more applications such as data, voice, and video, and the implementation of the multi-network integration policy, it is becoming more and more urgent to break through the access network bandwidth "bottleneck" and access distance restrictions. Only to break through the access network bandwidth "bottlenecks" "With the restriction of access distance, the entire network can effectively play the role of bandwidth, truly promote the development of various services, and bring economic and social benefits to operators. PON (Passive Optical Network), as a suitable access technology, is rapidly and widely used in this context. As a traditional network networking method, switches are widely used in enterprise networks, but they can no longer meet the requirements of multiple fields, multiple services, high bandwidth, high reliability, and high convenience. The EPON/GPON networking method is in video Monitoring, fiber to the home, campus network, and industrial communication network have received more and more attention and applications. Its low cost, simple maintenance, easy expansion, easy upgrade, high security, multi-service and other features are highly regarded by operators and integrated The likes and trust of businessmen. The following comparative analysis of the two is as follows: 1. Principle comparison PON (802.3ah) is a passive optical network based on Ethernet. The content it carries is Ethernet data packets. Therefore, PON is born to serve IP. Like the traditional LAN technology standards, all are funded by IEEE. Data transmission principle PON The downstream uses 1490nm light waves to carry data. The downstream data between the OLT (optical line terminal) and the ONU (optical network unit) uses point-to-multipoint broadcast to transmit data (TDM), and the ONU identifies the data of the LLID of the MPMC layer of the message. Between the OLT and ONU, AES-128 is used for encryption to ensure data security. For upstream data from ONU to OLT, time division multiple access technology (TDMA) is used to allocate time slots for each ONU to transmit upstream traffic. After the ONU is successfully registered, the OLT will configure a specific bandwidth for the ONU according to the system configuration (using DBA, the OLT will dynamically allocate bandwidth to each ONU according to the specified bandwidth allocation strategy and the status report of each ONU). For the PON level, bandwidth refers to how many basic time slots can transmit data, and the unit time length of each basic time slot is 16nm. Under each OLT port (PON port), the clocks between all ONUs and the OLT PON port are strictly synchronized. Each ONU can only start at the time when the OLT allocates it, and transmits data with the length of the time slot allocated to it. . Through time slot allocation and delay compensation, it is ensured that when the data signals of multiple ONUs are coupled to an optical fiber, the upstream packets of each ONU will not interfere with each other. LAN is a kind of local area network technology, which is introduced into the access network due to its simple technology and wide use. The current LAN technology is mainly Ethernet, especially IEEE802.3u and IEEE802.3z/ab are widely used. Ethernet using CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Monitoring) is a shared technology. In this technology, the devices at both ends are equal, and both parties use the same mechanism to transmit data traffic. The data exchange between the terminal and the terminal is forwarded on the switch completely in accordance with the MAC, and the data is forwarded by CSMA/CD. The emergence of VLAN has solved the problems of conflicts and broadcasts. Bandwidth and transmission distance LAN Ethernet currently achieves a symmetrical access rate of 10/100/1000Mbit/s, but it can only provide a transmission distance of up to 200m. This is also one of the biggest problems as an access technology. It is usually smart through The cascade switch extends the transmission distance. PON also achieves a symmetric access rate of 10/100/1000Mbit/s, but can guarantee a transmission distance of up to 20km, completely overcomes the limitations of Ethernet and xDSL technology in distance and bandwidth, and enables broadband access solutions to cover The scope is wider. Networking capability and scalability. LAN equipment is placed in an office building or a residential area and connects users through Category 5 cables, which involves the overhead of wiring projects in the building. Experience shows that the equipment and wiring in the early stage occupy a lot of manpower and material resources, and the deployment of switches in the early stage of LAN access is in place at one time. If there is an error in the prediction of the number of users, the port will be idle for a long time, and it may also cause insufficient ports in some areas and trouble expansion . LAN is a point-to-point access technology of the system, which only supports point-to-point information transmission, so the networking has limitations. If there is a demand for broadband access along the narrow and long area, it is necessary to deploy switches at each demand point and integrate it into the central office aggregation switch, or place a secondary aggregation device at each demand point, which provides ports and sinks. Connect to the demand point switch traffic. If EPON technology is adopted, it is much faster to solve the demand. . PON is a point-to-multipoint access technology. After combining splitters with different splitting ratios, flexible networking can be realized, supporting tree, star, and chain networking. Along the narrow and long area with broadband access requirements, place a 1:2 passive optical splitter at each demand point. After planning a certain bandwidth, continue to lay the optical cable, and place a 1:2 passive optical cable at the next demand point. Splitter, so you can easily access all information nodes. The advantages of EPON supporting star networking are also obvious. A 1:N optical splitter can be placed in the ODN to cover the access of up to 64 information points, and the maximum coverage radius is 20km. PON products are mainly used in OLT and ONU. The OLT is arranged at the end of the computer room, and a set of OLT can cover a wide area. The passive equipment in the middle has low cost and can be deployed in place at one time. The ONU can be expanded with the development of the business. Moreover, the registration of ONUs on the OLT is automatically completed, so when an area needs to add ONUs, just join the network directly.
Nov 14, 2020
Leave a message
What Is The Difference Between Switched Ethernet Networking And PON Networking
Send Inquiry