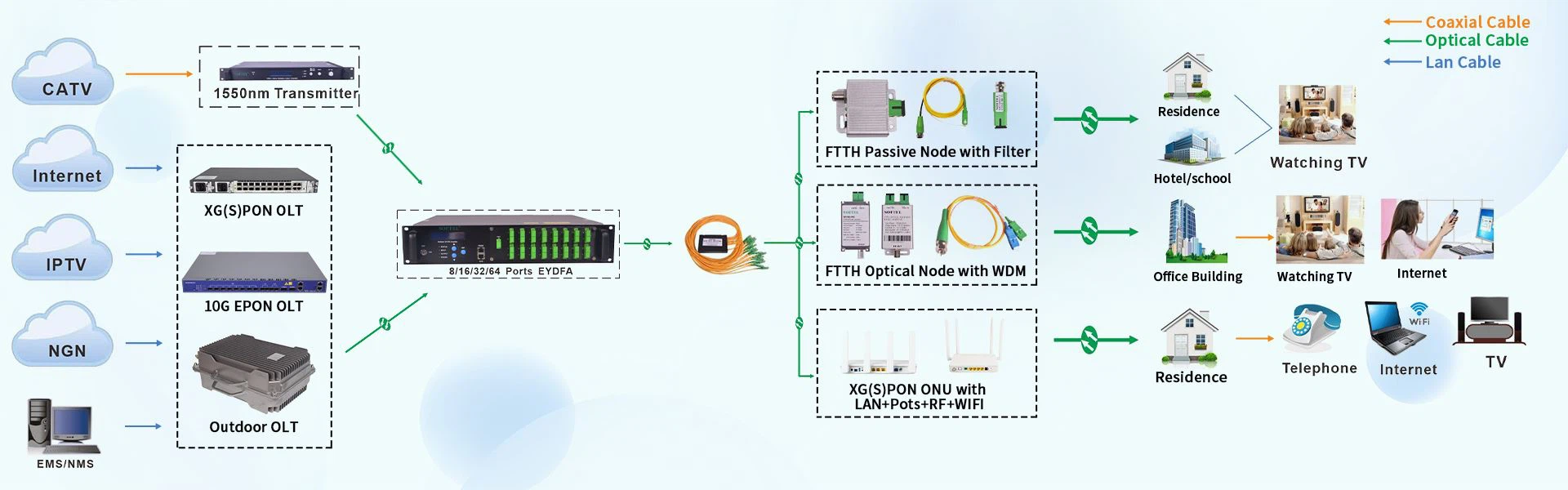
In networking, a headend refers to a central control point or a distribution center, especially in the context of cable television systems or broadband power line (BPL) networks. Here are the key points regarding headends in networking:
Central Control Point:
A headend serves as the central hub or control center of a network.
In cable television systems, it is the point where signals from various sources are received, processed, and then distributed to subscribers.
Signal Processing:
The headend receives signals from various sources, such as satellite feeds, local broadcast stations, and video servers.
These signals are then processed, which may include amplification, frequency conversion, modulation, demodulation, encoding, decoding, and other forms of signal conditioning.
Distribution:
After processing, the signals are distributed to subscribers via coaxial cables, fiber optic cables, or other transmission media.
The headend ensures that the signals are of the appropriate quality and format for transmission to end users.
BPL Network Manager:
In the case of BPL networks, the headend serves as the network's main station.
It provides dedicated access to manage the BPL network and also allows access to application IP networks.
The headend shares a simple AC power line network to provide power line/wireless LAN access to end users.
Digital Capabilities:
Modern headends are often digital, meaning they handle digital signals and support advanced features like high-definition television (HDTV), video-on-demand (VOD), and interactive services.
Digital headends often include functions for encoding and compressing digital content, as well as for digital signal processing and modulation.
In summary, a headend is a critical component of a network, especially in cable television and BPL systems, where it serves as the central hub for receiving, processing, and distributing signals to end users.